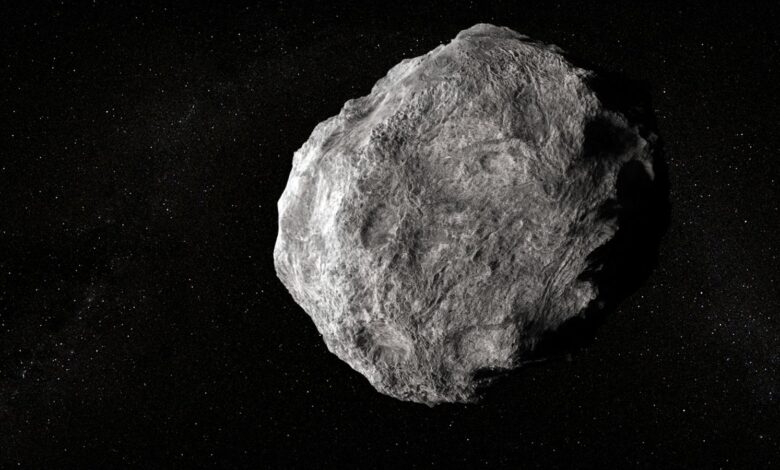
NASA has placed a warning on a giant-sized asteroid, which is huge in terms of dimensions and as big as a stadium. Measuring as big as a stadium, the asteroid is moving towards Earth at about 16 kilometers per second. Such close proximity of the asteroid to Earth is making scientists and ordinary citizens living in the world afraid of it. The facts of the asteroid and their implications in their impact through other measures to control the danger with such a report are discussed here:.
Properties of the Asteroid
The subject asteroid is classified as a Near-Earth Object, a category of objects that orbit the Sun and at one point reach within 1.3 astronomical units (AU) of Earth. The object in question has a diameter of about 300 meters, roughly the size of a big sports stadium, and is composed of rock, metal, and may have water ices. It’s moving at a speed of 16 kilometers per second, 57,600 kilometres per hour if you want to be more precise; faster than any man-made spacecraft and has multiplied the energy it would release some thousands of times if it were to reach Earth.
It falls under PHA categories, which essentially means space rocks whose orbits may take them close enough to Earth, causing damage on a considerable scale. While thousands of NEOs are monitored yearly, it’s the size and velocity of this space rock and the potential trajectory that makes it specially noticed.
Potential Impact and Consequences
The energy released from a collision with such an object and velocity would be apocalyptic. Though it is not as long as the one supposed to have caused the extinction of the dinosaurs, it could still cause massive destruction. Estimatedly, the impact will come with several hundred megatons of TNT, which makes the force more potent than the nuclear explosion ever seen on Earth.
In this case, if it were to hit land, the impact would produce an enormous crater, with more significant damage structures and loss of life in a radius of a few hundred kilometers. Dust and debris pushed into space could probably disrupt global climate patterns and lead to a “nuclear winter” effect. An over-the-ocean strike would create massive tsunamis, which could displace millions of people and ruin coastal cities.
However, with such vast space, the likelihood of it hitting a populated area is relatively low. Still, damage from even a less direct impact or near-miss would be tremendous in terms of shockwaves and atmospheric effects that can be felt from the entire globe.
NASA Monitoring and Mitigation Activities
Since its discovery, NASA has monitored the asteroid directly using its Planetary Defense Coordination Office (PDCO). By using data from radar and optical telescopes, scientists could track the path of the asteroid clearly for a clear determination of its trajectory. The main mission of the PDCO is to detect, track, and characterize potentially hazardous asteroids and comets and develop strategies concerning planetary defense.
The orbit of the asteroid would appear to be a convergence with Earth, according to NASA observations; however, whether it will hit or pass safely by Earth is not yet clear. The path that this asteroid takes is determined by gravitationally interacting with other celestial bodies and a small forcing caused by the thermal emissions of the asteroid as it absorbs sunlight and radiates heat: the Yarkovsky effect.
Additional activities include tracking the asteroid. Here, NASA, among others, looks at various mitigation strategies. Deflection approaches, for example, involve using a spacecraft that makes the asteroid veer off course by a kinetic impactor-a process that has already been tested to success in NASA’s DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) mission. For this, a smaller asteroid was deliberately crashed into with a spacecraft to change its trajectory. It proved that such methods could work in diverting an asteroid if it is detected with enough time.
Global Response and Collaboration
This level of asteroid threat has obviously caused interagency and governmental cooperation around the world to grow. The United States, in coordination with the European Space Agency (ESA), China, and Russia, as part of a combined, international initiative, have come together to study, and even potentially counter, the asteroid threat. They are now tapping into that shared resource and sharing information in preparation to take joint action if called upon to do so.
The public has now taken an interest in monitoring asteroids, too. Hollywood movies have long portrayed impact by asteroids and comets in spectacular and larger-than-life scenarios. In comparison to such dramatization, real science behind planetary defense has become a topic of increased attention. Work is being done on public awareness campaigns to enlighten the public regarding the risks and the measures being taken to prevent such a catastrophe.
What’s Next?
As the asteroid draws closer, NASA and other space agencies will input that data into the model to fine-tune predictions of the trajectory for very precise trajectories that can determine whether the asteroid impact Earth or harmlessly pass Earth by. If necessary, the space agency will send launch deflection missions, which change the asteroid’s course.
While the current level of threat cannot be ascertained, the occurrence does draw attention to the importance of continuing investment in the areas of planetary defence research and technologies. Earth has received large impacts from asteroids already; it is only a matter of time before another significant object crosses our way again. The problem lies with these objects arriving at a time when their trajectories and potential impacts cannot be assessed sufficiently in time for proper preparation.
For now, the world watches and waits as NASA and the global scientific community work day and night to monitor and assess the situation, hoping for a near miss while preparing for all eventualities.
So, scary as the prospect of an asteroid of stadium-sized dimensions hurtling towards Earth is, NASA and all its international collaborations are doing everything in their power to protect the planet. Humanity is better prepared today than it ever has been to face off against and perhaps even deflect such threats from space. The next weeks and months will tell if it does so successfully, or not.